There is another airspace shape that we have not covered yet in our plugins 'family' to create airspaces: rectangle shape. Airspaces sometimes are defined as 'buffer' zone around line connecting two points or more points. Let's deal with the case that only two waypoints so far because this special case is quite often used as part of other more complex airspaces.
A humble outlet of my ideas of how to deal with repetitive task based on aeronautical data
Friday, 31 May 2019
Tuesday, 28 May 2019
Dealing with obstacles data stored in CSV files (1)
Authorities sometimes publishes obstacle data sets called eTOD, which stands from Electronic Terrain and Obstacle Data. Those data sets comes in various formats: csv files, dat files, xml files (AIXM format) or even shapefiles.
This post will start a mini-series which result will be a QGIS plugin to import eTOD data from CSV files into PostGIS database.
This post will start a mini-series which result will be a QGIS plugin to import eTOD data from CSV files into PostGIS database.
Tuesday, 21 May 2019
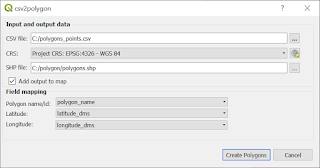
QGIS Plugin: csv2polygon
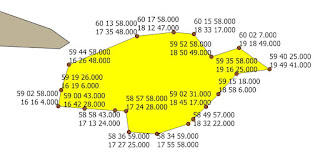
Another plugin that takes data stored in CSV file. This time you can create polygon. It is especially useful, when you have tabular data that describes polygon (e. g. airspace) as pair of latitude an longitude values. The biggest advantage is that you can create many polygons in one run of a plugin.
Saturday, 18 May 2019
AviationLatLonCalculator enhancement: user can choose which CSV field is what
Fields from CSV file have been assigned to its values from CSV header file (e .g. BRNG, DIST) inside the code so far. User has to prepare input file with 'correct' header - otherwise won't be able to perform calculations. And this is a big disadvantage.
Let's assume that we have following data set:
Let's assume that we have following data set:
Sunday, 5 May 2019
Parsing NASR data: NAV file
Let's start with defining the fields that values we want to extract from data file. Notice that this for the time being, only some basic data we want to extract so, dictionary contains only one 'subdictionary' NAV1. For more information refer to file description.
navaid_fields = {'NAV1': {'NAVAID_FAC_TYPE': (20, 9), 'NAVAID_NAME': (30, 43), 'NAVAID_LAT': (14, 372), 'NAVAID_LON': (14, 397), 'MAG_VAR': (5, 480), 'MAG_VAR_EPOCH_YEAR': (4, 485), 'CHANNEL': (4, 530), 'FREQUENCY': (6, 534)} }
Tuesday, 30 April 2019
Parsing NASR data: APT file (landing facility data)
Dictionary that keeps information about 'fields boundary' of attributes we want to extract looks as follows:
apt_fields = {'APT': {'FAC_TYPE': (13, 15), 'LOC_IDENTIFIER': (4, 28), 'EFF_DATE': (10, 32), 'CITY_NAME': (40, 94), 'OFFICIAL_NAME': (50, 134), 'ARP_LAT': (15, 524), 'ARP_LON': (15, 551), 'ARP_ELEV': (7, 579), 'MAG_VAR': (3, 587), 'MAG_VAR_EPOCH_YEAR': (4, 590), 'ARFF_TYPE_DATE': (15, 843), 'FUEL_TYPE': (40, 901), 'REPAIR_SERVICES': (5, 941), 'BOTTLED_OXYGEN': (8, 951), 'BULK_OXYGEN': (8, 959) }, 'ATT': {'ATTENDENCE_SCHEDULE': (108, 19)} }
Saturday, 6 April 2019
QGIS Plugin AviationPolygonCreator
As the name suggests with this plugin will be helpful to create polygons that are common in various aeronautical publications and other legal documents. The result of this plugin will be, of course, polygon, from which you will be able to derived WKT string and use it to build airspaces with all attributes, that are relevant for your project. A brief introduction to the problem of 'airspace shapes' you can find in this post: Airspaces - grouping by shape.
Wednesday, 27 March 2019
How to 'convert' table from pdf to csv (example of extracting points)
Let's imagine that you have pdf files with some data. You need to extract some of this data for further processing: e. g. file contains table with points with some attributes such as name and your goal is to get points layer from this file. If tables are nicely formatted in the way that if you copy and paste them into text file you will get something that looks like a 'table', I have a good news for you: there is no need to use extra libraries of tools to extract desired data. You can extract data manually by using spreadsheet for example (which is something we are not going to do), websites which converts pdf into other format and etc. You can also take advantage of the fact, that copied table is 'nicely' formatted and write parser that will extract desired data. It is worth to do that, if we are going to process data in cycles, for example parts of AIP.
Sunday, 24 March 2019
Monday, 18 March 2019
CoordinateExtractor Plugin: improvements
However CoordinateExtractorPlugin work as we expect - there are still some features that are missing that significantly increase capability of getting pairs of coordinates from plain text. The first is quite obvious - user should be able to define her or his own latitude-longitude separator. (I might have implemented only this option from the beginning actually). The second one comes form the fact, that there are possible some deviation from the pattern of coordinates, such as variable number of blank characters as latitude-longitude separator, or in the string that is latitude-longitude separator.
First, we need to change a bit GUI for dialog:
for comboBoxCoordSeparator add new item 'User defined'
new QLineEdit: lineEditUserSeparator
new QCheckBox: checkBoxReomveBlanks
Method that sets separator between latitude and longitude has to be changed, so it will takes user defined separator:
First, we need to change a bit GUI for dialog:
for comboBoxCoordSeparator add new item 'User defined'
new QLineEdit: lineEditUserSeparator
new QCheckBox: checkBoxReomveBlanks
Method that sets separator between latitude and longitude has to be changed, so it will takes user defined separator:
def set_latlon_separator(self): if self.dlg.comboBoxCoordSeparator.currentIndex() == 0: self.dlg.lineEditUserSeparator.setEnabled(False) self.latlon_separator = None elif self.dlg.comboBoxCoordSeparator.currentIndex() == 1: # Null separator self.dlg.lineEditUserSeparator.setEnabled(False) self.latlon_separator = cet.SEP_NULL elif self.dlg.comboBoxCoordSeparator.currentIndex() == 2: # Space self.dlg.lineEditUserSeparator.setEnabled(False) self.latlon_separator = cet.SEP_SPACE elif self.dlg.comboBoxCoordSeparator.currentIndex() == 3: # Hyphen self.dlg.lineEditUserSeparator.setEnabled(False) self.latlon_separator = cet.SEP_HYPHEN elif self.dlg.comboBoxCoordSeparator.currentIndex() == 4: self.dlg.lineEditUserSeparator.setEnabled(False) self.latlon_separator = cet.SEP_SLASH elif self.dlg.comboBoxCoordSeparator.currentIndex() == 5: self.dlg.lineEditUserSeparator.setEnabled(False) self.latlon_separator = '\\' elif self.dlg.comboBoxCoordSeparator.currentIndex() == 6: self.dlg.lineEditUserSeparator.setEnabled(True) self.latlon_separator = self.dlg.lineEditUserSeparator.text()
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)